Learn more about cyber rights, how to keep your data secure, and what you can do to advocate for stronger online privacy laws.
Index
- Definition and explanation of cyber rights
- Historical evolution of cyber rights
- How data collection is impacting our privacy
- What are the different ways to secure your digital data?
- What can you do to keep your data secure?
- The role of governments, companies, and citizens in defending cyber rights
- How AI and automation are changing the face of cyber security and our digital liberties?
- Conclusions

Has someone posted private material online without your permission?
Request immediate assistance
Definition and explanation of cyber rights
Cyberspace is a borderless world that needs to be regulated.
Much like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights the online world should be extended to include these human rights where it applies to all Internet users.
EU Agency for Cybersecurity Executive Director, Juhan Lepassaar stated that:
“Today’s global context is inevitably driving major changes in the cybersecurity threat landscape. The new paradigm is shaped by the growing range of threat actors”.
The online security of citizens is constantly endangered: their rights, their freedom of expression, their dignity.
There is no solid definition of cyber rights but we can define them as the fundamental rights of every individual to make use of the digital space while ensuring and preserving their human and civil rights.
According to the European Union’s Digital Rights Declaration, cyber rights can be defined as human rights on the Internet.
The most important cyber rights include:
- Right to privacy;
- The right to information;
- Right to freedom of expression;
- The right to be forgotten;
- Protection of Minors;
- Protection of Human dignity online.
There are always new cyber risks that threaten these rights, from unlawful government processing of personal data to cybercriminal attacks.
CRO Cyber Rights Organization works to monitor these risks and protect cyber rights in every digital platform, especially when a cyber criminal violates a person’s freedom.
Common misconceptions about cyber rights and why we need to be better informed
Often, we are led to believe that our digital identities are safe only because they are protected inside a smartphone.
Today more than ever, cyber rights have to be at the heart of European and international political debate and agendas.
Very often we don’t realize that the biggest problem with cyber rights is their implication in people’s lives.
According to research by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime costs the world $8 trillion a year: it includes personal data breaches, sextortion, doxing and the so-called revenge porn.

A major misconception is indeed underestimating the harm that cyber rights violations can bring to people’s private lives.
For example, dissemination of non consensual intimate images (NCII), sextortion, and cyberbullying are some of the biggest cyber rights abuses.
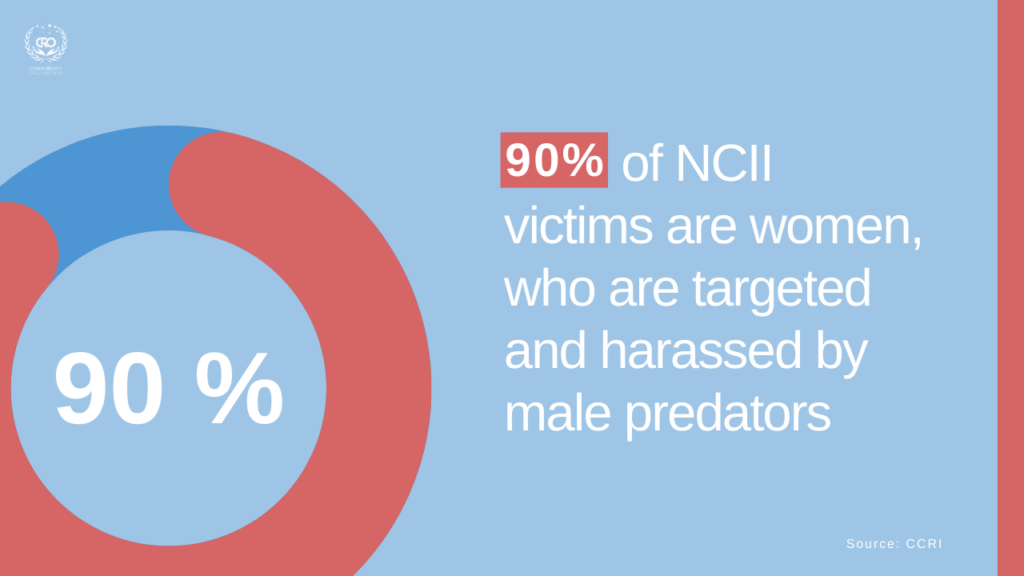
According to a CCRI report, 90% of NCII victims are women, who are disproportionately targeted and harassed by male predators in a variety of online settings, forums, chat rooms, websites, social media.
Therefore, to underestimate the damage that some violations could have against a specific population group could be dramatic.
This is why, educating on the importance of cyber rights online, providing educational paths to schools, is fundamental.
The majority of digital crimes that violate cyber human rights result in cases of cyberbullying.
UNICEF defines it as:
“Any aggressive, intentional act carried out by a group or individual, using electronic forms of contact, against a victim who cannot easily defend himself or herself. Typically, cyberbullying is carried out repeatedly and over time, and is characterized by an imbalance of power.”
Power imbalance, use of electronic or digital means, anonymity, and the capacity for mass communication are the characteristics of this crime
The biggest misconception is therefore believing that cyber rights do not interfere with people’s digital lives.
Historical evolution of cyber rights
Laws must be adapted to protect and uphold fundamental rights in the age of digitalization.
Digital rights, which are closely linked to freedom of expression and privacy, are those rights that allow people to access and use computers, other electronic devices and communication networks.
Digital rights simply extend the rights outlined in the UN’s Universal Declaration of Human Rights to the online realm.
In this regard, at least with respect to the right to personal data protection, supranational bodies such as the European Union (EU) are proposing a common framework.
For instance, the GDPR, enacted in 2018, requires member countries to both protect citizens’ personal information and allow data to move freely.
The GDPR was an important step in the direction of preserving and safeguarding the cyber rights of European citizens.
But even more than the GDPR is the declaration on digital rights and principles for everyone in the EU.
As can be read in the preamble:
“The draft declaration on digital rights and principles aims to give everyone a clear reference point about the kind of digital transformation Europe promotes and defends. It will also provide a guide for policy makers and companies when dealing with new technologies”.
Approved in January 2022, it served to protect the freedoms of European citizens on the Internet and to lay the foundations for the sustainable development of new technologies and digital spaces.
Cyber rights have benefited greatly from this European milestone that has now inspired international lawmakers.
How data collection is impacting our privacy
As stated in an article published by the Journal of Physic that studied the effect of privacy concerns on individuals’ decisions to share personal information:
“The rapid developments and innovations in technology have created unlimited opportunities for private and public organizations to collect, store and analyze the large and complex information about users and their online activities.”
For this reason, the privacy of personal information is still the subject of considerable controversy.
The problem is that big data analytics methods unlawfully generate, store, and process user data, leaving users with little to no control over their personal information.
A security breach of personal data shall result in the destruction, loss, modification, unauthorized disclosure or access to the personal data transmitted, stored or otherwise processed.
According to Statista, in 2022, there were 1802 data breaches in the United States, compared to 785 incidents in 2015.

The number of people affected by these breaches gradually decreased between 2019 and 2021.
For many people, data collection is an invasion of their privacy and a practice that can easily be abused, which is a source of mistrust and suspicion for many companies.
In the past year, 70% of companies, in KPMG‘s survey, have increased their collection of personal data from consumers.
About 75% of the business leaders surveyed said that they are comfortable with the amount of data that their company is collecting.

The privacy of citizens and their data are exposed to an unbridled collection of information that takes place, sometimes without a request for permission.
In a way, we are exposed to a great lack of protection of our personal data that can sometimes lead to practices that violate the digital rights of the person.
What can we do about it?
A personal data breach may compromise the confidentiality, integrity or availability of personal data.
Some possible examples:
- Access to or acquisition of data by unauthorized third parties;
- The theft or loss of computer equipment containing personal data;
- The deliberate alteration of personal data;
- Inability to access data due to accidental causes or external attacks, viruses, malware, etc.
- The loss or destruction of personal data due to accidents, adverse events, fires or other disasters
- Unauthorized disclosure of personal data.
The data controller (public entity, undertaking, association, party, professional, etc.) must notify the personal data protection authority of the breach.
Unless the personal data breach is unlikely to pose a risk to the rights and freedoms of natural persons.
In addition, if the infringement entails a high risk for the rights of individuals, the holder must communicate it to all data subjects.
To prevent this type of violation and mitigate the uncontrolled collection of personal data, you must always keep under control the logs and use platforms that can manage and effectively examine them and not grant permissions to unknown or suspicious links.
The CRO Cyber Rights Organization aims to raise awareness through training and guest lectures for NGOs and professionals.
It is only by acting together on a global scale that change can happen.
What are the different ways to secure your digital data?
Microsoft Blog illustrate a few tips to make sure your files are safe and accessible when you need them:
- Keep everything up to date;
- Create a secure password;
- Use an encrypted hard drive;
- Encrypt your mobile device;
- Add security information to your cloud storage account.
More importantly, keep in mind that all citizens should adhere to three core elements of data security:
- Confidentiality: ensures that only authorized users with proper credentials access data;
- Integrity: ensures that all stored data is reliable, accurate, and not altered inappropriately;
- Availability: ensures that data is easily accessible and available for ongoing business needs.
Everybody can keep their devices and accounts safe from unwanted outside access and protect your privacy from those you don’t want to share your information with by making a few simple changes.
And this allows you to see guaranteed and armored before all your digital rights, and secondly to reduce the likelihood of running into cyber threats.
In this perspective, CRO Cyber Rights Organization has always endeavored to contribute to the cybersecurity awareness of the users.

Are you a victim of online crime or abuse?
Contact the CRO Helpline
What can you do to keep your data secure?
Backing up your data is one of the most basic, yet often overlooked, tips for data protection.
Basically, this means making a duplicate copy of your data.
This way, if your device is lost, stolen, or compromised, you won’t lose your important information.
Whether you’re a small business owner, an individual, or a family, it’s always a good idea to secure your wireless network with a password.
This will prevent unwanted people from hijacking your wireless network.
When you delete your information from a computer, it is rarely the case that the information is truly gone forever.
The majority of applications offer user privacy settings that control the amount and type of information that is exchanged and stored.
You should always choose to share as little information as possible.
Bluetooth technology has brought incredible benefits to the mobile world, but it also opens the door to vulnerability.
Most Bluetooth exploits depend on an active Bluetooth connection; it is therefore important, turn it off in case you are not using it.
These are some precautions that can help reduce the likelihood of a data breach.
The role of governments, companies, and citizens in defending cyber rights
McKinsey states that in the world, every second, more than 127 devices are connected to an internet network.

The exposure of citizens and businesses to risks of cyber attacks or violation of their digital rights is high.
To address the cybersecurity risks facing their citizens, businesses, and critical infrastructure, more than 100 governments have developed national cybersecurity defense strategies.
The World Economic Forum has identified three key ways that governments can put into action to protect themselves against cyber attacks and citizens’ cyber rights:
- Adapting national cyber security policy frameworks;
- Improving international cooperation;
- Implementing ongoing education initiatives to raise cyber security awareness.
The idea of a protective government requires taxes for financing, training, and equipping IT structure for a well-trained cyber-police.
To this extent, there is also a need to protect the individual citizen from violations against their digital dignity.
On 23 November 2001, the Council of Europe approved the Budapest Convention which is the first true legal document governing crimes committed through the Internet or electronic networks.
As can be read in the premise of the Convention:
“It serves as a guideline for any country wishing to draw up comprehensive legislation to combat cybercrime, and as a framework for co-operation between its States Parties”.
This convention, together with the European Digital Rights and Principles, has made possible a great common effort to protect cyber rights in Europe.
How AI and automation are changing the face of cyber security and our digital liberties?
AI prevents new attacks through autonomous systems and learning patterns, unlike traditional cybersecurity techniques that only detect known threats.
Even when only partially deployed, AI outperforms traditional systems; this significantly minimizes the threat.
It will then identify deviations from the norm or security events before they can be addressed.
These patterns can help improve security in the future, identifying and blocking similar potential threats in advance.
Here are some examples of AI applied to cyber security:
- Home Security Systems;
- CCTV cameras and crime prevention;
- Credit card fraud detection and risk mitigation;
- Border control security;
- AI-powered biometric technology.
AI technology drives much of what we do from morning to night as we go about our daily routines.
It has become automatic and integral to the way we make decisions, plan and search for information.
While automation and AI have improved workers’ safety, lowered production costs, increased living well-being there are some important questions to ask.
High automation could drastically reduce the demand for jobs in industries.
Our societies can face social manipulation through the use of specific algorithms, jeopardizing the freedom of expression of the population.
Even social surveillance through AI technology poses serious doubts about the privacy of people and their freedom to oblivion and anonymity.
AI biases go far beyond gender and race.
In addition to data and algorithmic bias, the latter of which can amplify the former, AI is designed by humans – and humans are inherently biased.
All of these remarks pose serious cyber rights issues.
The task of civil society and organizations is to monitor that the development of AI and automation do not clash with the digital rights of people.
Conclusions
Cyber rights in recent years have effectively become an area of fundamental interest for the protection of citizens’ freedoms.
To protect them, we need to continue to develop legislation that coordinates cross states to defend and protect the dignity of man online.
You can draw the following conclusions by reading our guide:
- Cyber rights are the fundamental rights of every individual to make use of the digital space while ensuring and preserving their human and civil rights;
- The majority of digital crimes that violate cyber human rights result in cases of cyberbullying;
- Digital rights extend the rights outlined in the UN’s Universal Declaration of Human Rights to the online realm;
- The GDPR, enacted in 2018, requires member countries to both protect citizens’ personal information and allow data to move freely;
- All citizens should adhere to three core elements of data security: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability;
- The Budapest Convention which is the first true legal document governing crimes committed through the Internet or electronic networks;
- AI and automation are changing our lives from many points of view: sometimes for the better and sometimes for the worse for our digital freedoms.
CRO Cyber Rights Organization is committed daily to focus the attention of the international political agenda on the issue of cyber rights protection.
In addition, protecting and defending online crime survivors remains at the forefront of the activities accomplished by CRO.

Need help removing harmful or illegal content from the Internet?
Request immediate assistance

